Di Bitetti, M. S., Di Blanco, Y. E., Pereira, J. A., Paviolo, A., & Perez, I. J. (2009). Time partitioning favors the coexistence of sympatric Crab-eating Foxes (Cerdocyon thous) and Pampas Foxes (Lycalopex gymnocercus). Journal of Mammalogy, 90, 479-490.
Farias, A. A., & Kittlein, M. J. (2008). Small-scale spatial variability in the diet of pampas foxes (Pseudalopex gymnocercus) and human-induced changes in prey base. Ecological Research, 23, 543-550.
Garcia, V. B., & Kittein, M. J. (2005). Diet, habitat use, and relative abundance of pampas fox (Pseudalopex gymnocercus) in northern Patagonia, Argentina. Mammalian Biology, 70, 218-226.
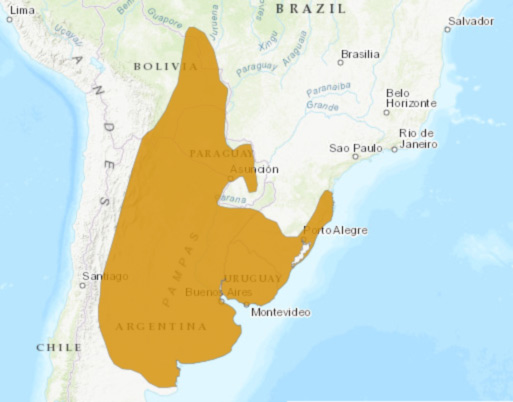
Lucherini, M., Pessino, M., & Farias, A. A. (2004). Pampas fox Pseudalopex gymnocercus (Fischer, 1814). In C. Sillero-Zubiri, M. Hoffmann & D. W. Macdonald (Eds.), Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan (pp. 63-68). Gland / Cambrigde: IUCN.