Crab-eating Fox
Cerdocyon thous
©Adriano Gambarini
Taxonomy
Standard English Name
Crab-eating Fox
Scientific Name
Cerdocyon thous
Brazilian common name/s
Cachorro-do-mato, graxaim-do-mato, raposa
Conservation status - IUCN
Physical Description
Is the best known of the Brazilian canids. Has a total length of 60 to 100 cm and weighs between 6 and 7 kg. Crab-eating foxes have a variable coloration, exhibiting a mixture of shades of gray and brown, often with yellowish tones. The ears are short with red tones. The tail is relatively long with long hairs tending to a black colouring.
Ecology and Habitat
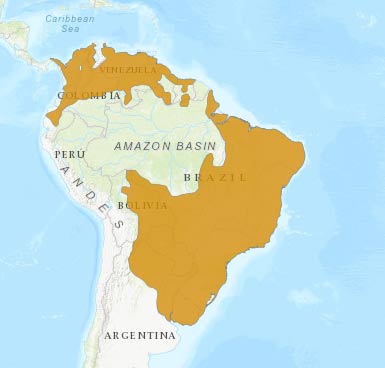
It is distributed widely across South America (excluding the Amazon basin), down as far as northern Argentina. It commonly inhabits open areas, fields and forests (mostly altered) and is mostly nocturnal. It’s a territorial animal and can occasionally be seen in pairs, although it does not hunt in groups.
Their diet varies depending on the season but generally consists of small mammals, birds, arthropods and fruits.
Gestation lasts 52 to 69 days, and the female gives birth to 3 to 6 puppies. The couple cares for and feed the pups that become independent at about 6 months old.
Online links
IUCN Canid Specialist Group – http://www.canids.org
Canid News – http://www.canids.org/canidnews/index.htm
References
Brady, C. A. (1979). Observations on the behavior and ecology of the crab-eating fox (Cerdocyon thous). In J. F. Eisenberg (Ed.), Studies of vertebrate zoology in the northern neotropics (pp. 161-171). Washington: Smithsonian Institute Press.
Bueno, A. D., & Motta, J. C. (2004). Food habits of two syntopic canids, the maned wolf (Chrysocyon brachyurus) and the crab-eating fox (Cerdocyon thous), in southeastern Brazil. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural, 77, 5-14.
Courtenay, O., & Maffei, L. (2004). Crab-eating fox Cerdocyon thous (Linnaeus, 1766). In C. Sillero-Zubiri, M. Hoffmann & D. W. Macdonald (Eds.), Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan (pp. ). Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK: IUCN/SSC Canid Specialist Group.
Facure, K. G., & Monteiro-Filho, E. L. A. (1996). Feeding habits of the crab-eating fox, Cerdocyon thous (Carnivora, Canidae), in a suburban area of southeastern Brazil. Mammalia, 60, 147-149.
Facure, K. G., Giaretta, A. A., & Monteiro-Filho, E. L. A. (2003). Food habits of the crab-eating-fox, Cerdocyon thous, in an altitudinal forest of the Mantiqueira Range, southeastern Brazil. Mammalia, 67, 503-511.
Gatti, A., Bianchi, R., Rosa, C. R. X., & Mendes, S. L. (2006b). Diet of two sympatric carnivores, Cerdocyon thous and Procyon cancrivorus, in a restinga area of Espirito Santo State, Brazil. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 22, 227-230.
Gatti, A., Bianchi, R., Rosa, C. R. X., & Mendes, S. L. (2006a). Diet of the crab-eating fox, Cerdocyon thous (Carnivora, Canidae) in Paulo Cesar Vinha State Park, Espirito Santo State, Brazil. Mammalia, 70, 153-155.
Juarez, K. M., & Marinho-Filho, J. (2002). Diet, habitat use, and home ranges of sympatric canids in Central Brazil. Journal of Mammalogy, 83, 925-933.
Macdonald, D. W., & Courtenay, O. (1996). Enduring social relationships in a population of crab-eating zorros, Cerdocyon thous, in Amazonian Brazil (Carnivora, Canidae). Journal of Zoology, 239, 329-355.
Michalski, F., Crawshaw, P. G., de Oliveira, T. G., & Fabian, M. E. (2006). Notes on home range and habitat use of three small carnivore species in a disturbed vegetation mosaic of southeastern Brazil. Mammalia, 70, 52-57.
Montgomery, G. G., & Lubin, Y. D. (1978). Social structure and food habits of crab-eating fox (Cerdocyon thous) in venezuelan llanos. Acta Cientifica Venezolana, 29, 382-383.
Pedo, E., Tomazzoni, A. C., Hartz, S. M., & Christoff, A. U. (2006). Diet of crab-eating fox, Cerdocyon thous (Linnaeus) (Carnivora, Canidae), in a suburban area of southern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 23, 637-641.
Rocha, V. J., Aguiar, L. M., Silva-Pereira, J. E., Moro-Rios, R. F., & Passo, F. C. (2008). Feeding habits of the crab-eating fox, Cerdocyon thous (Carnivora: Canidae), in a mosaic area with native and exotic vegetation in Southern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 25, 594-600.
Vasconcellos-Neto, J., de Albuquerque, L. B., & Silva, W. R. (2009). Seed dispersal of Solanum thomasiifolium Sendtner (Solanaceae) in the Linhares Forest, Espirito Santo state, Brazil. Acta Botanica Brasilica, 23, 1171-1179.
Vieira, E. M., & Port, D. (2007). Niche overlap and resource partitioning between two sympatric fox species in southern Brazil. Journal of Zoology, 272, 57-63.